 What Is Obesity?
What Is Obesity?
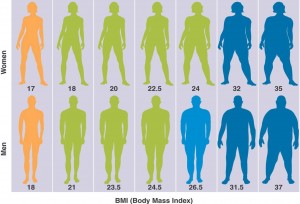
Obesity is an excess proportion of total body fat. A person is considered obese when his or her weight is 20% or more above normal weight. The most common measure of obesity is the body mass index or BMI. A person is considered overweight if his or her BMI is between 25 and 29.9; a person is considered obese if his or her BMI is over 30.
“Morbid obesity” means that a person is either 50%-100% over normal weight, more than 100 pounds over normal weight, has a BMI of 40 or higher, or is sufficiently overweight to severely interfere with health or normal function.
 Obesity is quickly becoming a major concern for a number of Western countries including the United States. While the prevalence of obesity is occurring all over the world, nowhere is this more true than the United States. A dramatic increase in the ingestion of foods that have less nutrients but more calories is one reason that is making obesity an American epidemic. It is a common misconception that this problem is limited to the United States. Other countries and regions such as China, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe are also experiencing high levels of increase in obesity. This epidemic can be directly related to food intake and the abysmal lack of exercise. An increasing number of children who watch television or play video games instead of engaging in physical activity are making obesity among children more common and more acceptable socially. The problem of epic obesity starts at early ages and mindful parents should be aware of how a child’s weight is progressing. A child who is currently obese between 10 and 13 stands an 80 percent chance of remaining obese through adulthood.
Obesity is quickly becoming a major concern for a number of Western countries including the United States. While the prevalence of obesity is occurring all over the world, nowhere is this more true than the United States. A dramatic increase in the ingestion of foods that have less nutrients but more calories is one reason that is making obesity an American epidemic. It is a common misconception that this problem is limited to the United States. Other countries and regions such as China, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe are also experiencing high levels of increase in obesity. This epidemic can be directly related to food intake and the abysmal lack of exercise. An increasing number of children who watch television or play video games instead of engaging in physical activity are making obesity among children more common and more acceptable socially. The problem of epic obesity starts at early ages and mindful parents should be aware of how a child’s weight is progressing. A child who is currently obese between 10 and 13 stands an 80 percent chance of remaining obese through adulthood.
 In the long term, obesity creates many additional problems apart from the social stigmata that is experienced. It is estimated that greater than 300,000 deaths per year are related to excessive weight gain because of limited exercise and poor eating habits. This translates to a societal cost of roughly $100 billion each year.
In the long term, obesity creates many additional problems apart from the social stigmata that is experienced. It is estimated that greater than 300,000 deaths per year are related to excessive weight gain because of limited exercise and poor eating habits. This translates to a societal cost of roughly $100 billion each year.
What Causes Obesity?
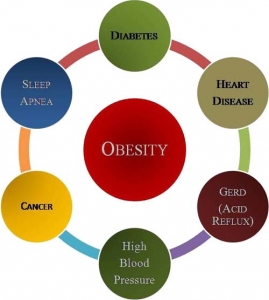
The causes of obesity begin with bad eating habits,when a person consumes more calories than he or she burns. But there are other factors that also play a role in obesity. These may include: binge eating, limited exercise, family history, illnesses, medications, life trauma, relationship problems, self-esteem, emotional problems, or many other issues that may cause a person to turn to food for comfort. From these early beginnings, obesity has many negative possibilities. An obese person is more at risk to develop heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, or other ailments.
Age.
As you get older, your body’s ability to metabolize food slows down and you do not require as many calories to maintain your weight. This is why people note that they eat the same and do the same activities as they did when they were 20 years old, but at age 40, gain weight.
 Gender.
Gender.
Women tend to be more overweight than men. Men have a higher resting metabolic rate (meaning they burn more energy at rest) than women, so men require more calories to maintain their body weight. Additionally, when women become postmenopausal, their metabolic rate decreases. That is partly why many women gain weight after menopause.
Environmental factors.
Although genes are an important factor in many cases of obesity, a person’s environment also plays a significant role. Environmental factors include lifestyle behaviors such as what a person eats and how active he or she is.
Physical activity.
Active individuals require more calories than less active ones to maintain their weight. Additionally, physical activity tends to decrease appetite in obese individuals while increasing the body’s ability to preferentially metabolize fat as an energy source. Much of the increase in obesity in the last 20 years is thought to have resulted from the decreased level of daily physical activity.
 Genetics.
Genetics.
Obesity (and thinness) tends to run in families. In a study of adults who were adopted as children, researchers found that participating adult weights were closer to their biological parents’ weights than their adoptive parents’. The environment provided by the adoptive family apparently had less influence on the development of obesity than the person’s genetic makeup. In fact, if your biological mother is heavy as an adult, there is approximately a 75% chance that you will be heavy. If your biological mother is thin, there is also a 75% chance that you will be thin. Nevertheless, people who feel that their genes have doomed them to a lifetime of obesity should take heart. Many people genetically predisposed to obesity do not become obese or are able to lose weight and keep it off.
Psychological factors.
Psychological factors also influence eating habits and obesity. Many people eat in response to negative emotions such as boredom, sadness, or anger. People who have difficulty with weight management may be facing more emotional and psychological issues; about 30% of people who seek treatment for serious weight problems have difficulties with binge eating. During a binge-eating episode, people eat large amounts of food while feeling they can’t control how much they are eating.
Illness.
Although not as common as many believe, there are some illnesses that can cause obesity. These include hormone problems such as hypothyroidism (poorly acting thyroid slows metabolism), depression, and some rare diseases of the brain that can lead to overeating.
Medication.
Certain drugs, such as steroids and some antidepressants, may cause excessive weight gain.
 Emotional Aspects of Obesity
Emotional Aspects of Obesity
One of the most painful aspects of obesity may be the emotional suffering it causes. American society places great emphasis on physical appearance, often equating attractiveness with slimness or muscularity. In addition, many people wrongly stereotype obese people as gluttonous, lazy, or both. However, more and more evidence contradicts this assumption. Obese people often face prejudice or discrimination at work, at school, while looking for a job, and in social situations. Feelings of rejection, shame, or depression are common.
When to Seek Help for Obesity
You should call your doctor if you are having emotional or psychological issues related to your obesity, need help losing weight, or if you fall into either of the following categories.
If your BMI is 30 or greater, you’re considered obese. You should talk to your doctor about your options for controlling your weight since you are at high risk of developing health problems.
If you have an “apple shape” — a so-called, “potbelly” or “spare tire” — you carry more fat in and around your abdominal organs. Fat deposited primarily around your middle increases your risk of many of the serious conditions associated with obesity. Women’s waist measurement should fall below 35 inches. Men’s should be less than 40 inches. If you have a large waist circumference, talk to your doctor about your options for permanent lose weight.